The pathogenesis of hip osteoarthritis
Anatomically, the hip joint consists of two bones:
- Ilium, with acetabulum;
- Femur, has a head. Doctors call the femur simply the femur.
Symptoms of hip osteoarthritis
The following symptoms are also typical:
- restricted activities;
- When a person tries to move the leg to the right (if we are talking about right-sided hip joint disease) or to the left (when the left joint is affected), then he will not be completely successful;
- The gait is usually different from that in healthy people and the patient has a limp;
- Loss of leg muscle mass;
- The affected leg becomes shorter.
Early stage osteoarthritis of hip joint
progress
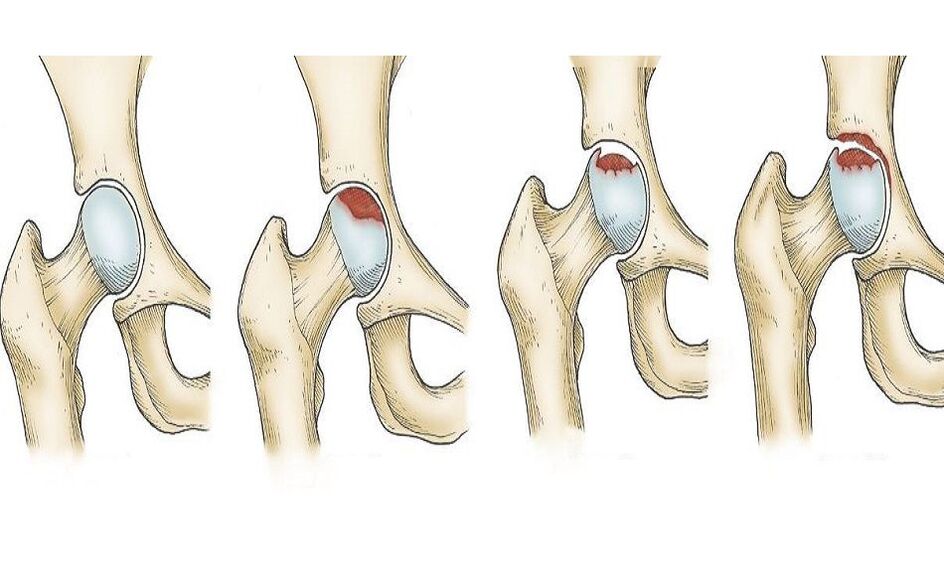
Late stage hip osteoarthritis
Diagnosis of Hip Osteoarthritis
It is carried out through a comprehensive inspection which includes:
- The doctor questions the patient;
- Checked by a doctor;
- Auxiliary examination, the main one is of course X-ray examination.
What might hip osteoarthritis be confused with?
This means that if such symptoms occur, doctors must first rule out the following conditions:
- Osteochondrosis (as it can also cause pain in the upper part of the leg);
- Knee osteoarthritis (presented by knee pain).
Treatment of Hip Arthropathy
Conservative treatment
This includes:
- Common analgesics, in the form of tablets to drink or injections (injections), ointments;
- Inject hormones into joints;
- Medications to restore cartilage structure (can also be taken orally or injected into the joint);
- Other medications prescribed by doctors based on the patient's condition. These include medications that relax muscles, dilate blood vessels, and more.



































